
Jordon Electronics
Jordon Electronics was located at 119 East Union Street in Pasadena, CA I 1955. It was a subsidiary of Panellit. The company was relocated to W. Mission Road in Alhambra, CA, and provided portable radiation monitors in 1959. In 1957, it was the Jordon Electronics Division of Victoreen Instruments Company. In 1955, Jordon instruments used the unique Neher-White ionization chamber. This chamber allows a single instrument to be used to measure common soil radioactivity up to those 15 million times as strong. Another exclusive feature was built in radiation check sources.

Jordan Electronics Logo 1955

Jordan Electronics Logo 1959

Jordon Electronics Radector Ad 1954
The Radector was introduced in 1953 as a gamma or gamma-beta portable meter. It can also use a separate probe for monitoring remote locations. It was the most widely used instrument for civil defense in 1955. The Model AG-500-SR and the Model AGB-500-SR have ranges 0.5 mR/h to 500 R/h. The Models AG-50-SR and AGB-50-Sr have range 0.05 mR/h to 50 R/h.
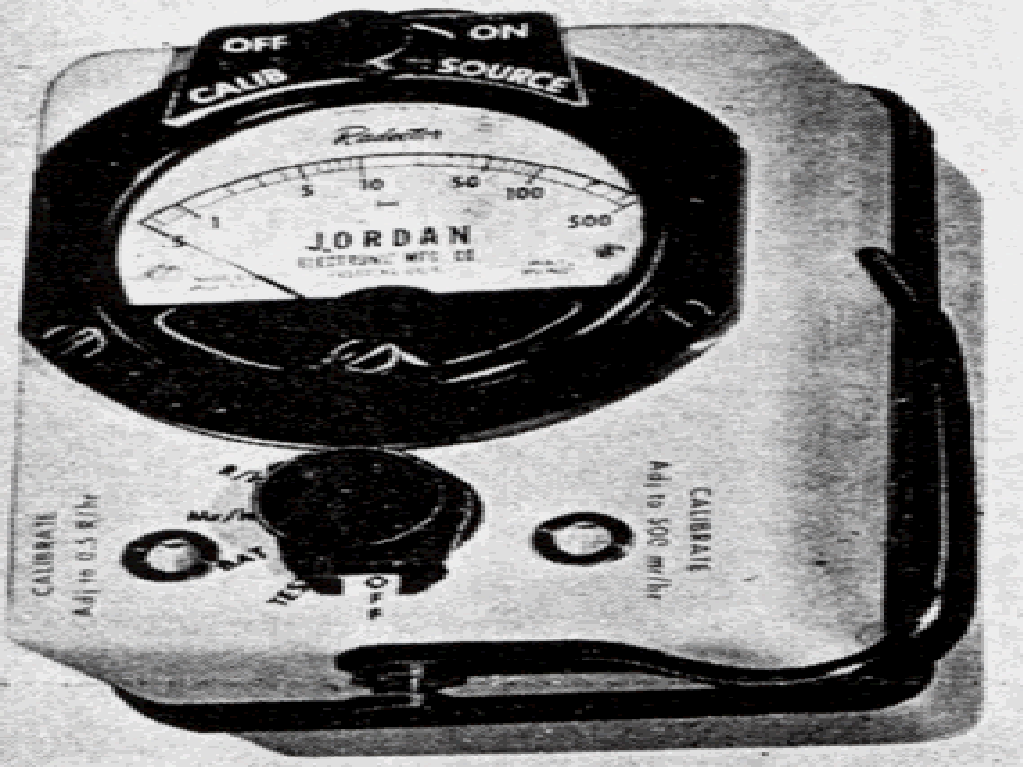
Jordon Electronics AGB-50-R Radector 1954
The Model AGB-50-SR “Radector” was introduced in 1954. It was a small meter that used the Neher-White ionization chamber. The SR models contained a Sr-90 source. The range was 0.05-50 mR/h and 0.05-50 R/h. The AGB-500-SR had a range from 0.5-500 mR/h and 0.5-500 R/h. It used two 1.35V batteries and weighed 3 lbs. It sold for $167.50 in 1954.
In 1957, the Radector was offered with a separate probe for monitoring remote locations. The ionization chamber is high pressure, argon filled. The beta window is 1 mil stainless steel. The window opening is 0.5” diameter and had a steel beta rejection screen. The range is from 0.05 mR/h to 500 R/h. It also contained an embedded radioactive source. The unit weighed 3.5 lbs.
Need photo
Jordon Electronics AGB-50D-SR Radector 1957

Jordon Electronics AGB-500A-SR
The Models AG-50P and AG-500P were offered with an external ion chamber and 25’ cable.
The Model AG-500 Radector was introduced in 1953. It was replaced by the Model AGB-500-SR in 1954. It had an ion chamber with 10 atmospheres of argon. The ranges for the Model AG-50-SR was 0.05-50 mR/h and 0.05-50 R/h and the Model AG-500-SR was 0.5-500 mR/h and 0.5-500 R/h. The unit was small and weighed 3 lbs. It used two 1.35 volt batteries.


Jordon Electronics Ads 1954
The Radector 50B and 500B series was introduced in 1957. The 50B series consisted of AG-50B, AG-50B-SR, AG-50B-P, AGB-50B, AGB-50B-SR, and the AGB-50B-P. The 500B series consisted of the AG-500B, AG-500B-SR, AG-500B-P, AGB-500B, AGB-500B-SR, and the AGB-500B-P. The units are general purpose portable radiation monitoring instruments for use with high energy beta or gamma. These units are improved versions of the older 50 and 500 series. These units employ the Neher-White ionization chamber which has a sealed electrometer tube inside of the argon gas chamber. The units are not affected by humidity or altitude.
The 50B series measures from 0.05-50 mR/h and 0.05-50 R/h and the 500B series measures from 0.05-500 mR/h and 0.5-500 R/h. All units have both mR and R ranges, the 50B from 0.05-50 mR/h and 0.05-50 R/h and the 500B from 0.5-500 mR/h and 0.5-500 R/h. If the unit has a beta window, then the designation becomes AGB. The AGB models with the beta window closed are essentially the same gamma response as the AG models. If the designator has a P extension, then the unit has an external probe.
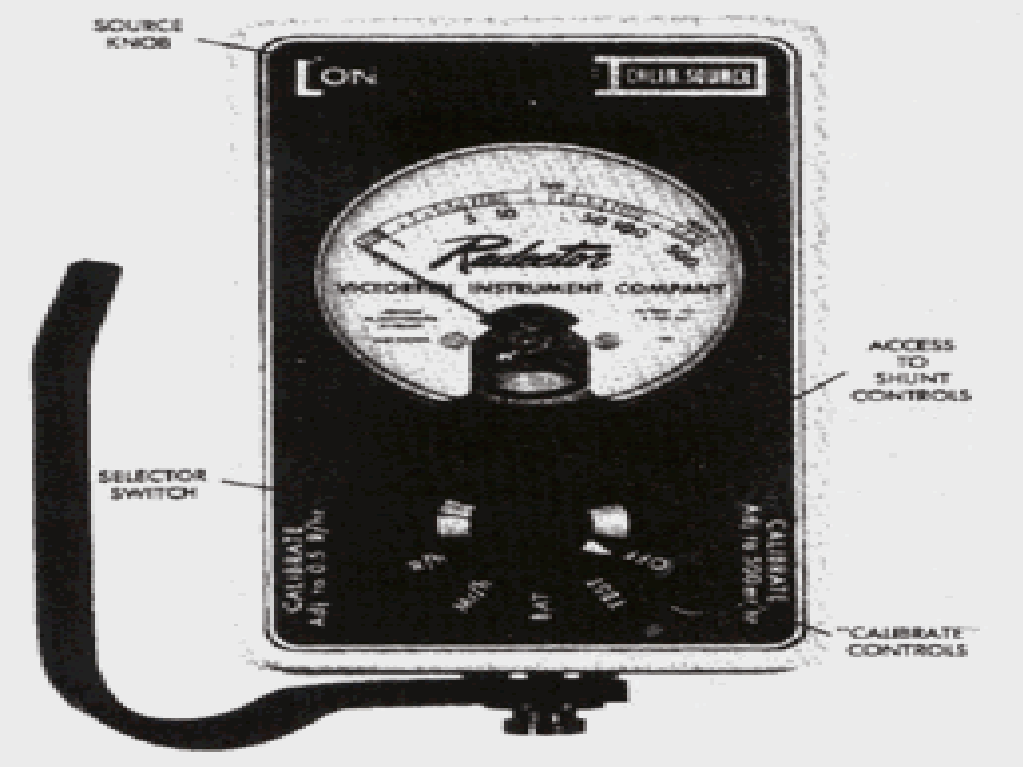
Radector Series 1957 (meter face shows Radector and Victoreen Instrument Company)
The SR designation means the unit has an internal strontium-90 source. The source can be activated by a knob above the meter face. The units measures 3.5” x 5” x 6” and weighs 3.5 lbs. It comes in a bright yellow painted color.


Jordon Electronics Ads 1956
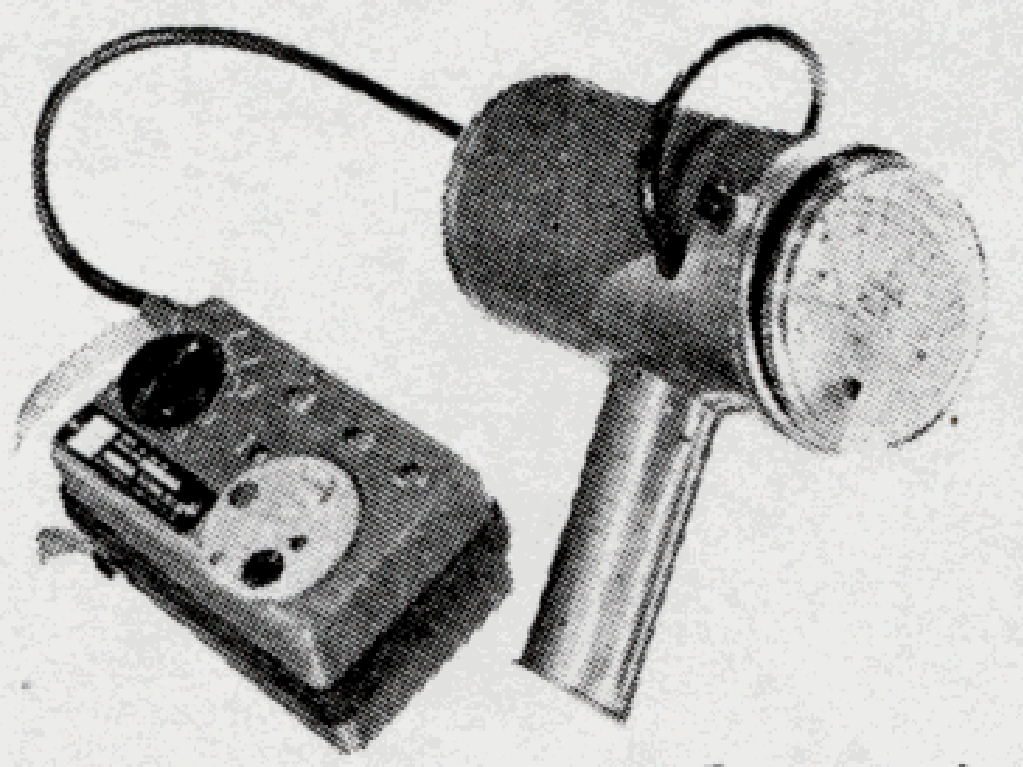
Jordon Electronics AGB-10 Scintillator 1954
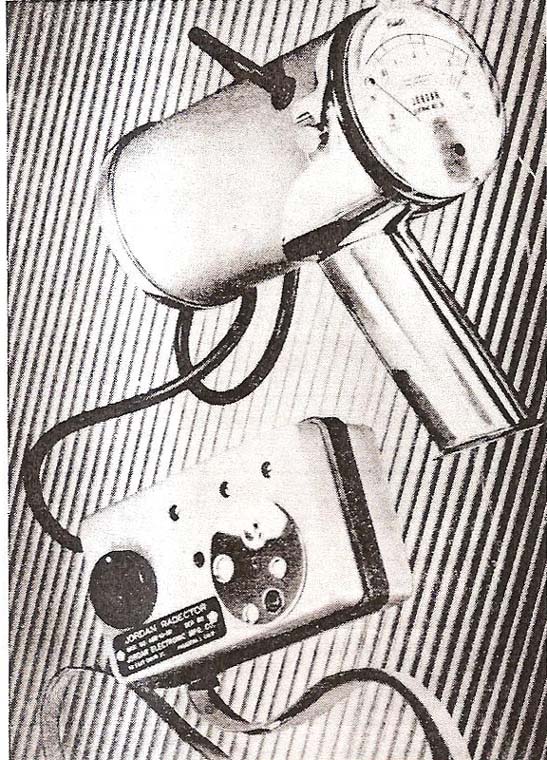
Jordon Electronics AGB-10 Scintillator 1954
The AGB-10 scintillator was introduced as a beta gamma survey instrument in 1954 with the Cutie Pie configuration. It could detect as small as 0.002 mR/h above background. It was a versatile, wide-range portable monitor. It has a built in calibration source and separable chamber. The ranges are from background to 10,000 R/h in a single instrument. The Model AGB-10-SR had a range from 0.01 mR/h to 10 R/h. The Model AGB-10K-SR has a range from 0.01 mR/h to 10,000 R/h.
The Model AGB-10-GP was a long probe survey meter for beta and gamma. It had a range from 0.01-10 mR/h and 10 mR/h-10 R/h. A third Model AGB-10K-GP had a range from 10-10,000 R/h. The gun type instruments without the probe but with same ranges are Model AGB-10-G and AGB-10K-G.
The Jordon Minirad was introduced in 1959. It was a miniature gamma dose rate meter. It was pocket size measuring 3.75" x 2.5" x 1.25" in thick and weighed less than 8 ounces. It had a wide logarithmic scale covering 0.005 R/h to 50 R/h (Model M-50), 0.01 R/h to 100 R/h (Model M-100) and 0.02 to 200 R/h (Model M-200), all with no switching required. It had simple pushbutton controls, one to test and one to read. Cost was $129.50.
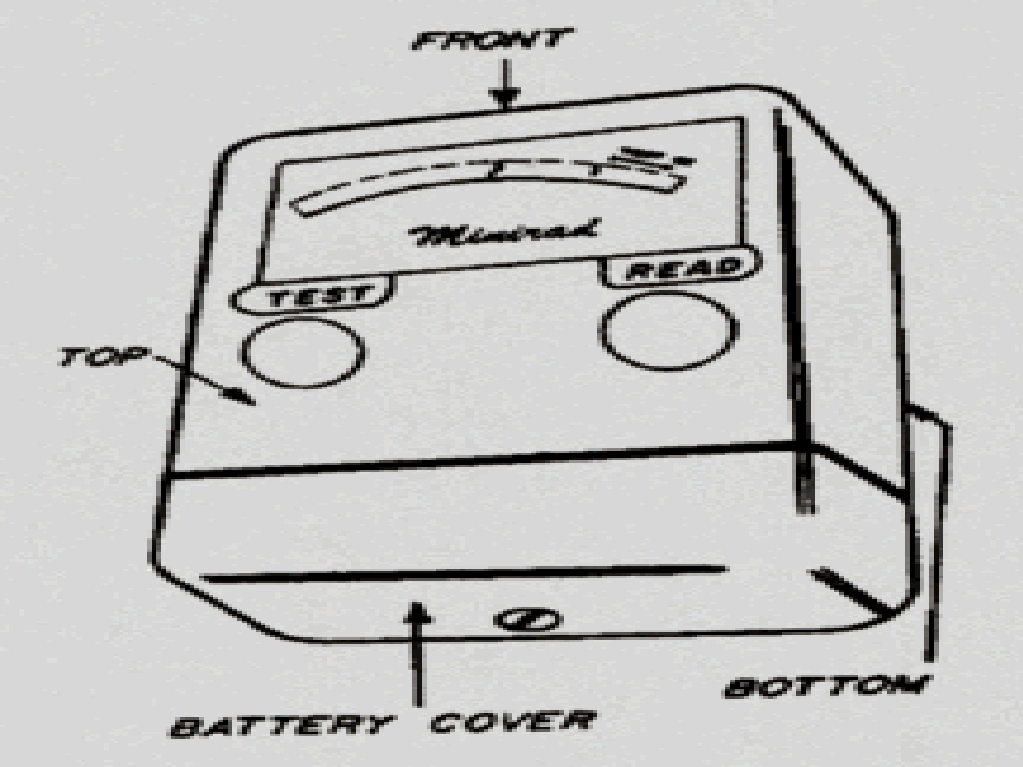
Jordon Electronics Minirad 1959
The Radector gamma-ray detector was sold in 1952 for civil defense use. It was small and could fit in the palm of your hand. The range was 0.02-500 R/h. It weighed 2 lbs. and battery life was nearly equal to the shelf life.
The Model AGB Radgun series was introduced in 1957. It was a high sensitivity portable monitor for health monitoring, food and water monitoring. The Model AGB-1G-SR has two ranges 0.01-1 mR/h and 1-100 mR/h. The Model AGB-10G-SR has two ranges from 0.01-10 mR/h and 0.01-10 R/h. The Model AGB-10KG-SR has three ranges from 0.01-10 mR/h, 0.01-10 R/h and 10-10,000 R/h. All three are identical and use a logarithmic scale on the meter. The SR stands for strontium-90 which is included with each unit for checking the calibration. The sources are hermetically sealed either strontium-90 or krypton-85 which give preset calibration check points. The Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) recommended a swipe leak test every six months. All units manufactured prior to 1965 will most likely contain a Sr-90 source.
It has the widest range of any survey meter of the time ranging from 0.01 mR/h to 10,000 R/h. The unit had a bright gold color. It will detect increments as small as 0.002 mR/h above background. It used a Neher-White ionization chamber which was steel walled and filled with 10 atmospheres of argon. The Neher-White chamber is different from other ion chambers in that the output directly drives the indicating meter. The outside of the steel chamber is covered by a thin sheet of lead to ensure responses independent of energy from 80 keV to 1.2 MeV.
The chamber could be detached and attached to a six foot extension probe or 50’ cable. The SR in the model designator indicated the unit contained a Sr-90 radioactive source of less than 1 microcurie. The unit weighs 4.5 lbs and used three 1.34, one 5 and three 30 volt batteries. The model AGB-1G-SR had two ranges from 1 and 100 mR/h and the Model AGB-10G0SR had two ranges from 10 mR/h and 10 R/h.

Jordon Electronics Radgun AGB-10KG-SR 1957
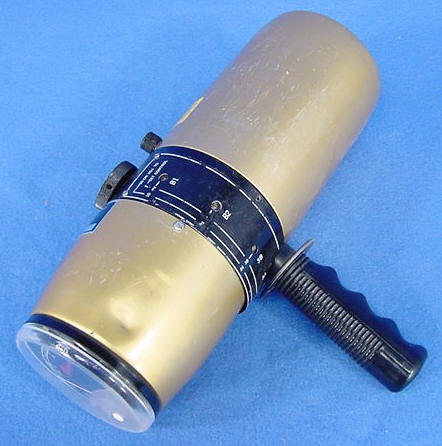



Jordon Electronics Radgun AGB-10KG-SR 1957
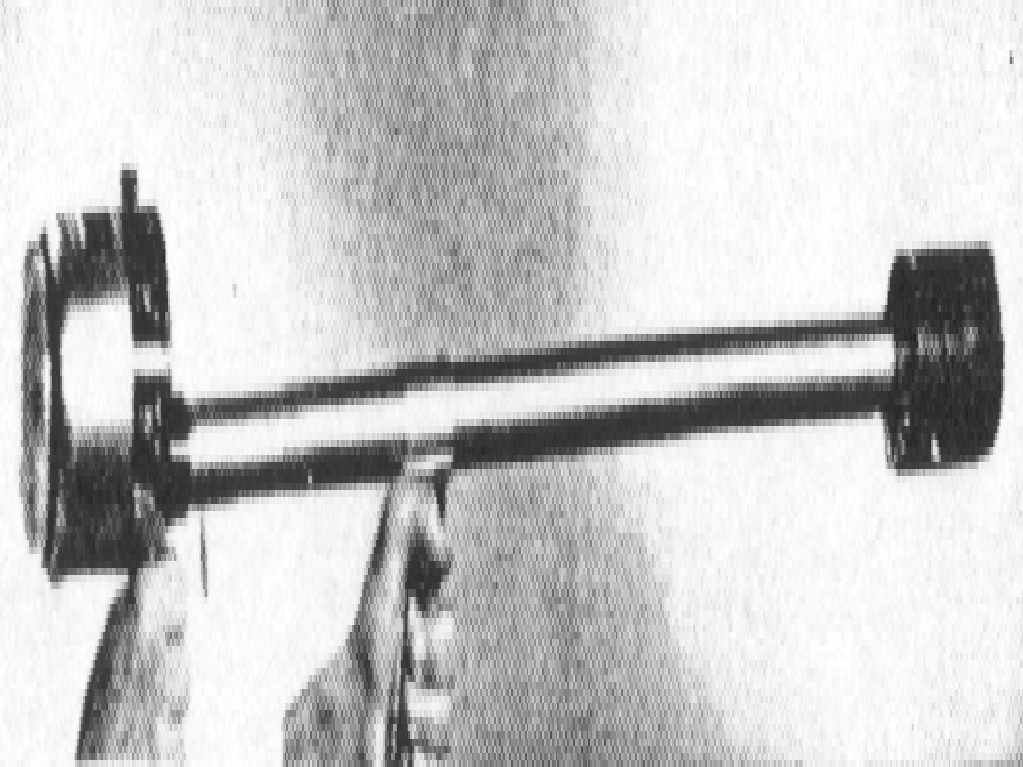
Jordon Electronics Long Probe ABG-10-GP 1956
The Minirad was produced in three Models M-80, M-100 and M-200 in the 1950's as a radiac meter. It was a miniature gamma dose rate meter for personnel protection use. The unit uses a Neher-White ionization chamber with argon gas.
Need photo
Minirad Model M Series

Jordon Electronics Ad 1959